C There are two C 4 H 5 N 2 O formula units in caffeine, so the molecular formula must be (C 4 H 5 N 2 O) 2 = C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2. The structure of caffeine is as follows: Exercise 3.4.3: Freon-114. Calculate the molecular formula of Freon-114, which has 13.85% carbon, 41.89% chlorine, and 44.06% fluorine.
Empirical Formulas. – ppt download
Combustion analysis can only determine the empirical formula of a compound; it cannot determine the molecular formula. However, other techniques can determine the molecular weight. Once we know this value, coupled with the empirical formulas, we can easily calculate what the molecular formula is. … Example #4: Caffeine has the following

Source Image: chem.libretexts.org
Download Image
Empirical Formulas. An empirical formula tells us the relative ratios of different atoms in a compound. The ratios hold true on the molar level as well. Thus, H 2 O is composed of two atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. Likewise, 1.0 mole of H 2 O is composed of 2.0 moles of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of oxygen.We can also work backwards from molar ratios since if we know the molar amounts of

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations – 18 Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime Aug 2, 2022onurdongel / Getty Images By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated on August 02, 2022 The empirical formula of a compound is defined as the formula that shows the ratio of elements present in the compound, but not the actual numbers of atoms found in the molecule. The ratios are denoted by subscripts next to the element symbols.

Source Image: diffzy.com
Download Image
Of The Following The Only Empirical Formula Is
Aug 2, 2022onurdongel / Getty Images By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated on August 02, 2022 The empirical formula of a compound is defined as the formula that shows the ratio of elements present in the compound, but not the actual numbers of atoms found in the molecule. The ratios are denoted by subscripts next to the element symbols. Solution: 1) Assume 100 g of the compound is present. This changes the percents to grams: S —> 50.05 g O —> 49.95 g 2) Convert the masses to moles: S —> 50.05 g / 32.066 g/mol = 1.5608 mol O —> 49.95 g / 16.00 g/mol = 3.1212 mol 3) Divide by the lowest, seeking the smallest whole-number ratio:
Empirical Formula vs. Molecular Formula – What’s The Difference (With Table)
A 24.81g sample of a gaseous compound containing only carbon, oxygen, and chlorine is determined to contain 3.01 g C, 4.00 g O, and 17.81 g Cl. … Following the same approach yields a tentative empirical formula of: … The empirical formula mass for this compound is approximately 30 amu (the sum of 12 amu for one C atom, 2 amu for two H Determine the empirical formulas of the compounds with the follo… | Channels for Pearson+

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
Empirical Formula Calculations | How to Find Empirical Formula A 24.81g sample of a gaseous compound containing only carbon, oxygen, and chlorine is determined to contain 3.01 g C, 4.00 g O, and 17.81 g Cl. … Following the same approach yields a tentative empirical formula of: … The empirical formula mass for this compound is approximately 30 amu (the sum of 12 amu for one C atom, 2 amu for two H
Source Image: chemistrynotes.com
Download Image
Empirical Formulas. – ppt download C There are two C 4 H 5 N 2 O formula units in caffeine, so the molecular formula must be (C 4 H 5 N 2 O) 2 = C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2. The structure of caffeine is as follows: Exercise 3.4.3: Freon-114. Calculate the molecular formula of Freon-114, which has 13.85% carbon, 41.89% chlorine, and 44.06% fluorine.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations – 18 Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime Empirical Formulas. An empirical formula tells us the relative ratios of different atoms in a compound. The ratios hold true on the molar level as well. Thus, H 2 O is composed of two atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen. Likewise, 1.0 mole of H 2 O is composed of 2.0 moles of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of oxygen.We can also work backwards from molar ratios since if we know the molar amounts of

Source Image: dreamstime.com
Download Image
Empirical Formula – Easy Science | Chemistry basics, Study chemistry, Chemistry classroom The empirical formula for a compound is C 2 H 5 and its relative formula mass is 58. Deduce its molecular formula. Deduce its molecular formula. ( A r of C = 12, A r of H = 1)

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
1:33 calculate empirical and molecular formulae from experimental data – TutorMyself Chemistry Aug 2, 2022onurdongel / Getty Images By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated on August 02, 2022 The empirical formula of a compound is defined as the formula that shows the ratio of elements present in the compound, but not the actual numbers of atoms found in the molecule. The ratios are denoted by subscripts next to the element symbols.
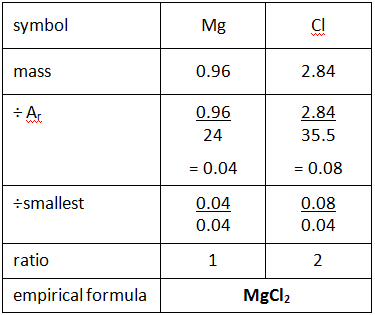
Source Image: tutormyself.com
Download Image
Empirical and Molecular Formulae | A Level Chemistry Revision Solution: 1) Assume 100 g of the compound is present. This changes the percents to grams: S —> 50.05 g O —> 49.95 g 2) Convert the masses to moles: S —> 50.05 g / 32.066 g/mol = 1.5608 mol O —> 49.95 g / 16.00 g/mol = 3.1212 mol 3) Divide by the lowest, seeking the smallest whole-number ratio:

Source Image: twinklsecondary.blog
Download Image
Empirical Formula Calculations | How to Find Empirical Formula
Empirical and Molecular Formulae | A Level Chemistry Revision Combustion analysis can only determine the empirical formula of a compound; it cannot determine the molecular formula. However, other techniques can determine the molecular weight. Once we know this value, coupled with the empirical formulas, we can easily calculate what the molecular formula is. … Example #4: Caffeine has the following
Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations – 18 Empirical Formula Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart – Dreamstime 1:33 calculate empirical and molecular formulae from experimental data – TutorMyself Chemistry The empirical formula for a compound is C 2 H 5 and its relative formula mass is 58. Deduce its molecular formula. Deduce its molecular formula. ( A r of C = 12, A r of H = 1)