Solution: Step 1: Measure OP. Step 2: Extend the line OP to the point P’ such that OP’ = 2OP. Step 3: Repeat the steps for all the vertices: point Q to get Q’ and point R to get R’. Step 4: Join the points P’Q’R’ to form the image. Example: Enlarge triangle ABC with C as the center of dilation and a scale factor of 3.
Textbooks :: Mathspace
Let’s consider a quadrilateral in the coordinate plane. Performing a dilation of requires three vital pieces of information: The coordinates of , , , and. The coordinates of the center of dilation, The scale factor of the dilation. With this information, we can dilate the vertices , , , and and then draw the corresponding segments to find the

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
Using your center C C and the scale factor you were given, draw the image under the dilation of each vertex of the polygon, one at a time. Connect the dilated vertices to create the dilated polygon. Draw a segment that connects each of the original vertices with its image.

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
Solved: 1. Dilate triangle ABC using center P and scale factor 3/2 . 2. What do the properties o [algebra] Step 1 To dilate triangle ABC with center P and scale factor 3/2, we will multiply the distance between eac… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Not the question you’re looking for? Post any question and get expert help quickly. Start learning Answer to Solved Respond to each question. a.

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
Dilate Triangle Abc Using Center P And Scale Factor 32.
Step 1 To dilate triangle ABC with center P and scale factor 3/2, we will multiply the distance between eac… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Not the question you’re looking for? Post any question and get expert help quickly. Start learning Answer to Solved Respond to each question. a. In middle school, students studied many examples of dilations and verified experimentally that dilations preserve angle measure. In this activity, students confirm this claim for one example, and recall what they know about dilations from middle school. Student Facing. Triangle is a dilation of triangle using center and scale factor 2.
A. Dilate triangle ABC using center p and scale factor 3/2. B. What do properties of dilations tell you – brainly.com
So we have this figure, this triangle ABC, A, B, C, right over here, and what we wanna do is dilate it, so that means scaling it up or down, and the center of that dilation is this point P. So one way to think about it is let’s think about the distance between point P and each of these points, and we wanna scale it by 1/4. Triangle is dilated using as the center of dilation with scale factor 2. The image is triangle A’B’C’. – brainly.com

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
On the figure below, sketch the image of triangle A’B’C’ by dilating using a scale factor of 3 with the center of dilation at the origin. Label the points A”B”C”. | Homework.Study.com So we have this figure, this triangle ABC, A, B, C, right over here, and what we wanna do is dilate it, so that means scaling it up or down, and the center of that dilation is this point P. So one way to think about it is let’s think about the distance between point P and each of these points, and we wanna scale it by 1/4.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Textbooks :: Mathspace Solution: Step 1: Measure OP. Step 2: Extend the line OP to the point P’ such that OP’ = 2OP. Step 3: Repeat the steps for all the vertices: point Q to get Q’ and point R to get R’. Step 4: Join the points P’Q’R’ to form the image. Example: Enlarge triangle ABC with C as the center of dilation and a scale factor of 3.
Source Image: mathspace.co
Download Image
Solved: 1. Dilate triangle ABC using center P and scale factor 3/2 . 2. What do the properties o [algebra] Using your center C C and the scale factor you were given, draw the image under the dilation of each vertex of the polygon, one at a time. Connect the dilated vertices to create the dilated polygon. Draw a segment that connects each of the original vertices with its image.
Source Image: gauthmath.com
Download Image
Solved: 1. Dilate triangle ABC using center P and scale factor 3/2 . 2. What do the properties o [algebra] Transcript. Dilations make a shape bigger or smaller. A scale factor tells us how much to multiply by the side lengths to change the size. The scale factor is the ratio of the side length in the new shape (image) to the side length in the corresponding side in the original shape (pre-image). Each pair of corresponding sides has the same factor.
![Solved: 1. Dilate triangle ABC using center P and scale factor 3/2 . 2. What do the properties o [algebra]](https://p16-ehi-va.gauthmath.com/tos-maliva-i-ejcjvp0zxf-us/7f9862d542da4b1f8bd4c6b8a9c22a87~tplv-ejcjvp0zxf-gwm-webp-scale:1125:312.webp)
Source Image: gauthmath.com
Download Image
triangle ABC is being dilated with center of dialation at the origin. The image of c, point C’, has – brainly.com Step 1 To dilate triangle ABC with center P and scale factor 3/2, we will multiply the distance between eac… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Not the question you’re looking for? Post any question and get expert help quickly. Start learning Answer to Solved Respond to each question. a.

Source Image: brainly.com
Download Image
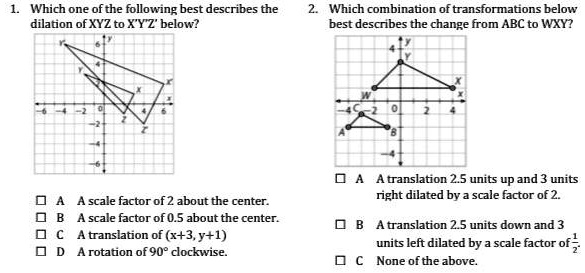
SOLVED: Which one of the following best describes the dilation of XYZ to XYZ’ below? Which combination of transformations below best describes the change from ABC to WXY? Translation 2.5 units up In middle school, students studied many examples of dilations and verified experimentally that dilations preserve angle measure. In this activity, students confirm this claim for one example, and recall what they know about dilations from middle school. Student Facing. Triangle is a dilation of triangle using center and scale factor 2.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
On the figure below, sketch the image of triangle A’B’C’ by dilating using a scale factor of 3 with the center of dilation at the origin. Label the points A”B”C”. | Homework.Study.com
SOLVED: Which one of the following best describes the dilation of XYZ to XYZ’ below? Which combination of transformations below best describes the change from ABC to WXY? Translation 2.5 units up Let’s consider a quadrilateral in the coordinate plane. Performing a dilation of requires three vital pieces of information: The coordinates of , , , and. The coordinates of the center of dilation, The scale factor of the dilation. With this information, we can dilate the vertices , , , and and then draw the corresponding segments to find the
Solved: 1. Dilate triangle ABC using center P and scale factor 3/2 . 2. What do the properties o [algebra] triangle ABC is being dilated with center of dialation at the origin. The image of c, point C’, has – brainly.com Transcript. Dilations make a shape bigger or smaller. A scale factor tells us how much to multiply by the side lengths to change the size. The scale factor is the ratio of the side length in the new shape (image) to the side length in the corresponding side in the original shape (pre-image). Each pair of corresponding sides has the same factor.