For that reason alkyl radicals (generally considered to be sp 2 hybridized) are the most stable, followed by vinyl and phenyl radicals (sp-hybridized) , followed by alkynyl radicals.. 3. Radical Stability Decreases With Increasing Electronegativity of The Atom. Quiz time: Having read the paragraph above, what might you think is the effect of electronegativity on free radical stability?
Rank the following radicals in increasing order of their stability .D>C>B>AA>C>D>BA>B>C>DC>A>D>B
The hydroxyl radical, Lewis structure shown, contains one unpaired electron. Hydroxide ion compared to a hydroxyl radical. In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive.Many radicals spontaneously dimerize.

Source Image: foreo.com
Download Image
Jan 23, 202316936. In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valence electrons or an open electron shell, and therefore may be seen as having one or more “dangling” covalent bonds. With some exceptions, these “dangling” bonds make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Radical Stability and Free Radical Halogenation (Worksheet Solutions Walkthrough) – YouTube
3 is more stable than 4. Even though 4 is aromatic it is an aryl free radical the p orbital containing the radical is out of the plane and can’t be stabilized through resonance/Hyperconjugation. In fact I would say that option 4 is the least stable compound .
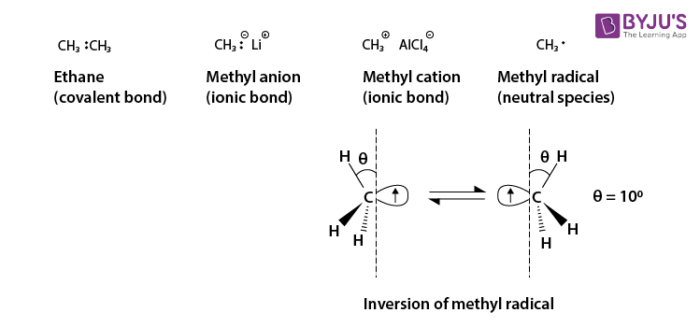
Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
Which Free Radical Would Be Least Stable
3 is more stable than 4. Even though 4 is aromatic it is an aryl free radical the p orbital containing the radical is out of the plane and can’t be stabilized through resonance/Hyperconjugation. In fact I would say that option 4 is the least stable compound .
Abstract. Free radicals and other oxidants have gained importance in the field of biology due to their central role in various physiological conditions as well as their implication in a diverse range of diseases. The free radicals, both the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), are derived from both endogenous
What are Free Radicals? – Definition, Examples, Types, Mechanism & Uses
1. Stability Of Free Radicals Increases In The Order Methyl < Primary < Secondary < Tertiary Let’s talk a bit about stability first, and then circle back to their structure. Being electron deficient, you might already have a hunch regarding factors that might stabilize free radicals.
Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria and Its Painful Impact
Source Image: neurodivergentinsights.com
Download Image
Peroxisome – free-radical scavengers – definition, structure, function, and biology
1. Stability Of Free Radicals Increases In The Order Methyl < Primary < Secondary < Tertiary Let’s talk a bit about stability first, and then circle back to their structure. Being electron deficient, you might already have a hunch regarding factors that might stabilize free radicals.
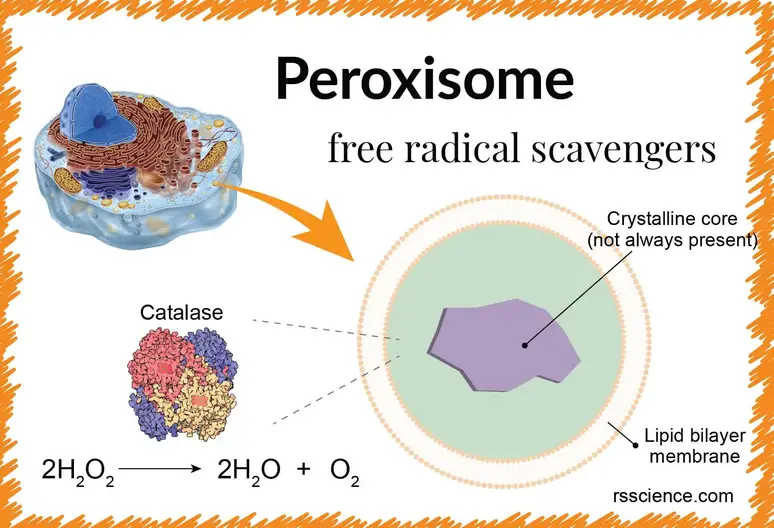
Source Image: rsscience.com
Download Image
Rank the following radicals in increasing order of their stability .D>C>B>AA>C>D>BA>B>C>DC>A>D>B
For that reason alkyl radicals (generally considered to be sp 2 hybridized) are the most stable, followed by vinyl and phenyl radicals (sp-hybridized) , followed by alkynyl radicals.. 3. Radical Stability Decreases With Increasing Electronegativity of The Atom. Quiz time: Having read the paragraph above, what might you think is the effect of electronegativity on free radical stability?
 Download Image
Download ImageRadical Stability and Free Radical Halogenation (Worksheet Solutions Walkthrough) – YouTube
Jan 23, 202316936. In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valence electrons or an open electron shell, and therefore may be seen as having one or more “dangling” covalent bonds. With some exceptions, these “dangling” bonds make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Artificial Neural Nets Finally Yield Clues to How Brains Learn | Quanta Magazine
Radical stability refers to the energy level of the radical. If the internal energy of the radical is high, the radical is unstable. It will try to reach a lower energy level. If the internal energy of the radical is low, the radical is stable. It will have little tendency to react further. Free radicals have only 7 electrons in their valence

Source Image: quantamagazine.org
Download Image
Understanding antioxidants – Harvard Health
3 is more stable than 4. Even though 4 is aromatic it is an aryl free radical the p orbital containing the radical is out of the plane and can’t be stabilized through resonance/Hyperconjugation. In fact I would say that option 4 is the least stable compound .

Source Image: health.harvard.edu
Download Image
Solved 1. Which free radical would be most stable? A) B) C) | Chegg.com
Abstract. Free radicals and other oxidants have gained importance in the field of biology due to their central role in various physiological conditions as well as their implication in a diverse range of diseases. The free radicals, both the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), are derived from both endogenous
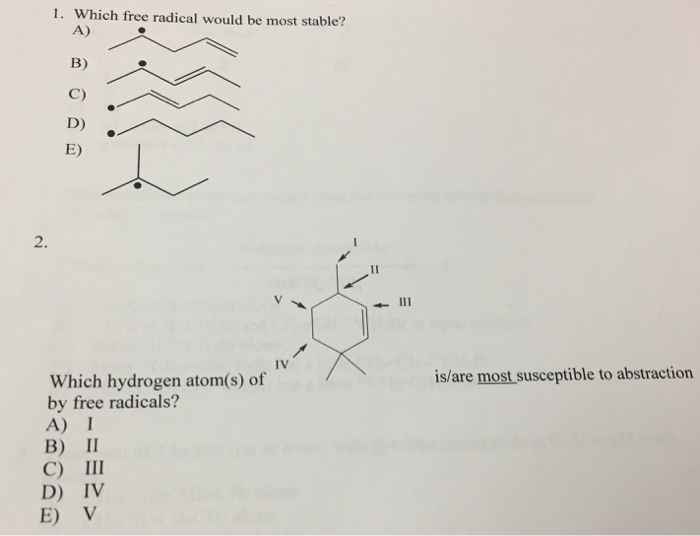
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Peroxisome – free-radical scavengers – definition, structure, function, and biology
Solved 1. Which free radical would be most stable? A) B) C) | Chegg.com
The hydroxyl radical, Lewis structure shown, contains one unpaired electron. Hydroxide ion compared to a hydroxyl radical. In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive.Many radicals spontaneously dimerize.
Radical Stability and Free Radical Halogenation (Worksheet Solutions Walkthrough) – YouTube Understanding antioxidants – Harvard Health
Radical stability refers to the energy level of the radical. If the internal energy of the radical is high, the radical is unstable. It will try to reach a lower energy level. If the internal energy of the radical is low, the radical is stable. It will have little tendency to react further. Free radicals have only 7 electrons in their valence