EXPERT VERIFIED Step 1/9 Step 1: Identify the acids in the given list. The acids in the given list are OH, NH, OH, CI, and 3. Step 2: Determine the pKa values of each acid. The pKa values of the acids are not provided in the given list. Therefore, we cannot directly rank them based on pKa values.
The correct decreasing order of pKa in the given compound is:
A pKa may be a small, negative number, such as -3 or -5. It may be a larger, positive number, such as 30 or 50. The lower the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more easily it gives up its proton. The higher the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more tightly the proton is held, and the less easily the proton is given up.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Predict the Outcome of Organic Acid-Base Reaction — Use pK a as Criterion With the knowledge of acidity and pK a, we are now ready to see how to apply this information to the understanding of organic reactions from an acid-base perspective.. The following reaction is an example in Section 3.2.If you take a closer look at the reactants and products, you will find that the “product” side

Source Image: dmd.aspetjournals.org
Download Image
Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and trained innate immunity | Science In this case, we need to rank these acids according to their expected p K a K_a K a values in order of highest p K a K_a K a to lowest p K a K_a K a .: ClCH 2 _2 2 COOH; ClCH 2 _2 2 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; CH 3 _3 3 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; Cl 2 _2 2 CHCOOH; All the compounds are carboxylic acids, therefore, they will lose
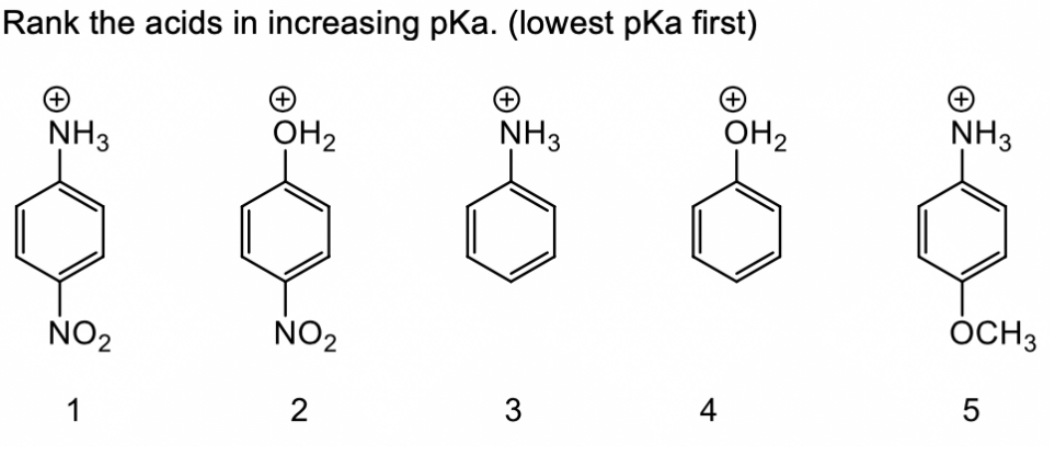
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Rank The Following Acids From Lowest Pka To Highest Pka
In this case, we need to rank these acids according to their expected p K a K_a K a values in order of highest p K a K_a K a to lowest p K a K_a K a .: ClCH 2 _2 2 COOH; ClCH 2 _2 2 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; CH 3 _3 3 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; Cl 2 _2 2 CHCOOH; All the compounds are carboxylic acids, therefore, they will lose Chemistry 10th Edition ISBN: 9781305957404 Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste Publisher: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste Chapter1: Chemical Foundations Section: Chapter Questions Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and
Answered: Rank the acids in increasing pKa.… | bartleby
Looking at Table 5.2. 1, you see that the pK a of carboxylic acids are in the 4-5 range, the pK a of sulfuric acid is -10, and the pK a of water is 14. Alkenes and alkanes, which are not acidic at all, have pK a values above 30. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid. Table 5.2. 1: Representative acid constants. Solved 13 Question ee page 330 (1 point) Rank the following | Chegg.com
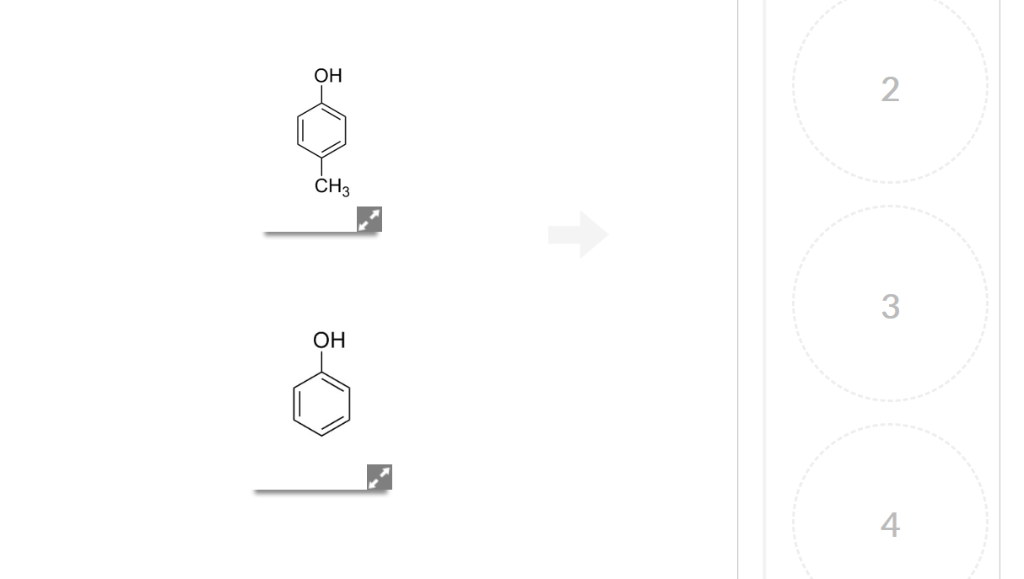
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Answered: Arrange the acids shown from lowest pKa… | bartleby Looking at Table 5.2. 1, you see that the pK a of carboxylic acids are in the 4-5 range, the pK a of sulfuric acid is -10, and the pK a of water is 14. Alkenes and alkanes, which are not acidic at all, have pK a values above 30. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid. Table 5.2. 1: Representative acid constants.
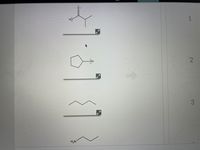
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
The correct decreasing order of pKa in the given compound is: EXPERT VERIFIED Step 1/9 Step 1: Identify the acids in the given list. The acids in the given list are OH, NH, OH, CI, and 3. Step 2: Determine the pKa values of each acid. The pKa values of the acids are not provided in the given list. Therefore, we cannot directly rank them based on pKa values.

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and trained innate immunity | Science Predict the Outcome of Organic Acid-Base Reaction — Use pK a as Criterion With the knowledge of acidity and pK a, we are now ready to see how to apply this information to the understanding of organic reactions from an acid-base perspective.. The following reaction is an example in Section 3.2.If you take a closer look at the reactants and products, you will find that the “product” side

Source Image: science.org
Download Image
Ranking Protons in order of Increasing Acidity Using pKa Values – YouTube 12 Rank the following molecules in order of increasing pKa (lowest pKa/most acidic to highest pKa/least acidic).

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
PPT – Acids & Bases/ Organic Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation – ID:1979697 In this case, we need to rank these acids according to their expected p K a K_a K a values in order of highest p K a K_a K a to lowest p K a K_a K a .: ClCH 2 _2 2 COOH; ClCH 2 _2 2 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; CH 3 _3 3 CH 2 _2 2 COOH; Cl 2 _2 2 CHCOOH; All the compounds are carboxylic acids, therefore, they will lose

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
14.9: Proton Donor Strength- pKa – Chemistry LibreTexts Chemistry 10th Edition ISBN: 9781305957404 Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste Publisher: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste Chapter1: Chemical Foundations Section: Chapter Questions Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and
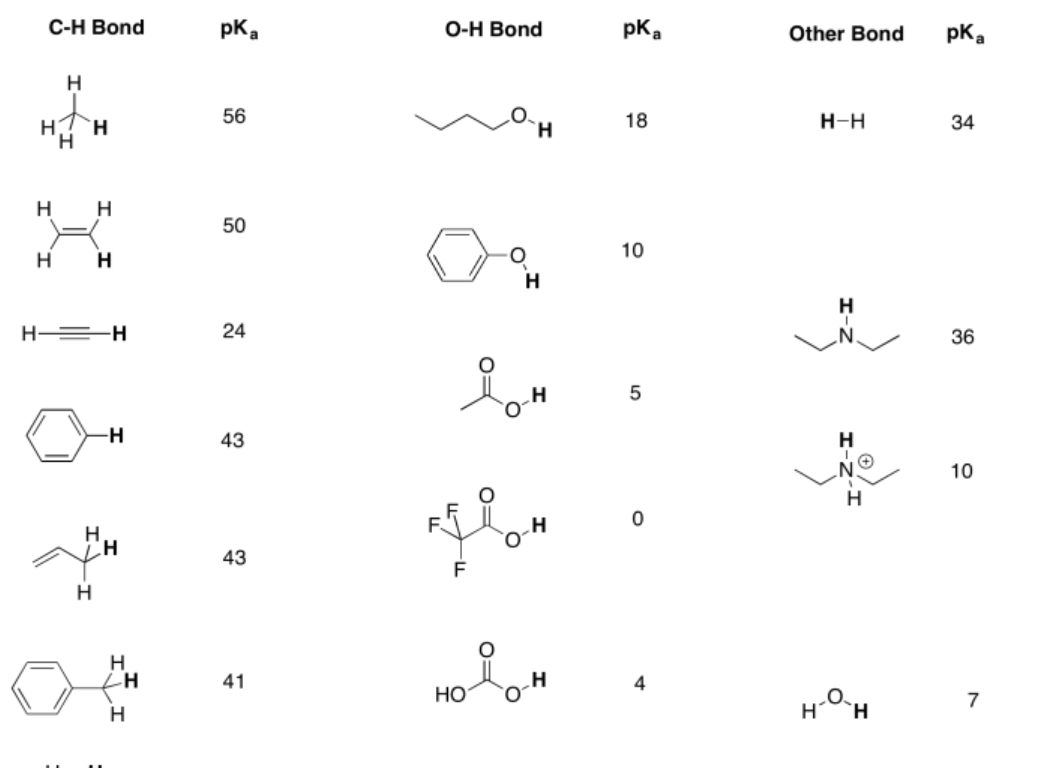
Source Image: chem.libretexts.org
Download Image
Answered: Arrange the acids shown from lowest pKa… | bartleby
14.9: Proton Donor Strength- pKa – Chemistry LibreTexts A pKa may be a small, negative number, such as -3 or -5. It may be a larger, positive number, such as 30 or 50. The lower the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more easily it gives up its proton. The higher the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more tightly the proton is held, and the less easily the proton is given up.
Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and trained innate immunity | Science PPT – Acids & Bases/ Organic Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation – ID:1979697 12 Rank the following molecules in order of increasing pKa (lowest pKa/most acidic to highest pKa/least acidic).